- Published on
Getting Started with Event-Driven Architectures in AWS using SNS, SQS, and EventBridge
- Authors

- Name
- Sneha Tuladhar
- @
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Core Concepts and Use Cases
- Service Comparison
- Integration Strategies with AWS Lambda
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
Introduction
Event-driven communication is a cornerstone of modern cloud architectures, enabling scalable, decoupled, and responsive systems.
AWS provides three core services to enable messaging and orchestration:
- Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) – enables real-time pub/sub messaging to multiple subscribers.
- Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) – provides message queuing to decouple microservices and ensure reliable delivery.
- Amazon EventBridge – intelligently routes events between AWS services or external systems based on rule-based filtering.
This guide explores their capabilities, practical use cases, and integrations with AWS Lambda to help you design scalable cloud-native solutions.
Core Concepts and Use Cases
1. Amazon SNS - Publish/Subscribe Model
Purpose: Distribute messages to multiple subscribers (fan-out) in real time.
Key Features:
- Supports email, SMS, HTTP/S, Lambda, and mobile push notifications.
- Ideal for broadcasting events to diverse endpoints.
Example Use Case: Order Confirmation System
Notify customers (via email) and backend services (via Lambda) when an order is placed.
Setup
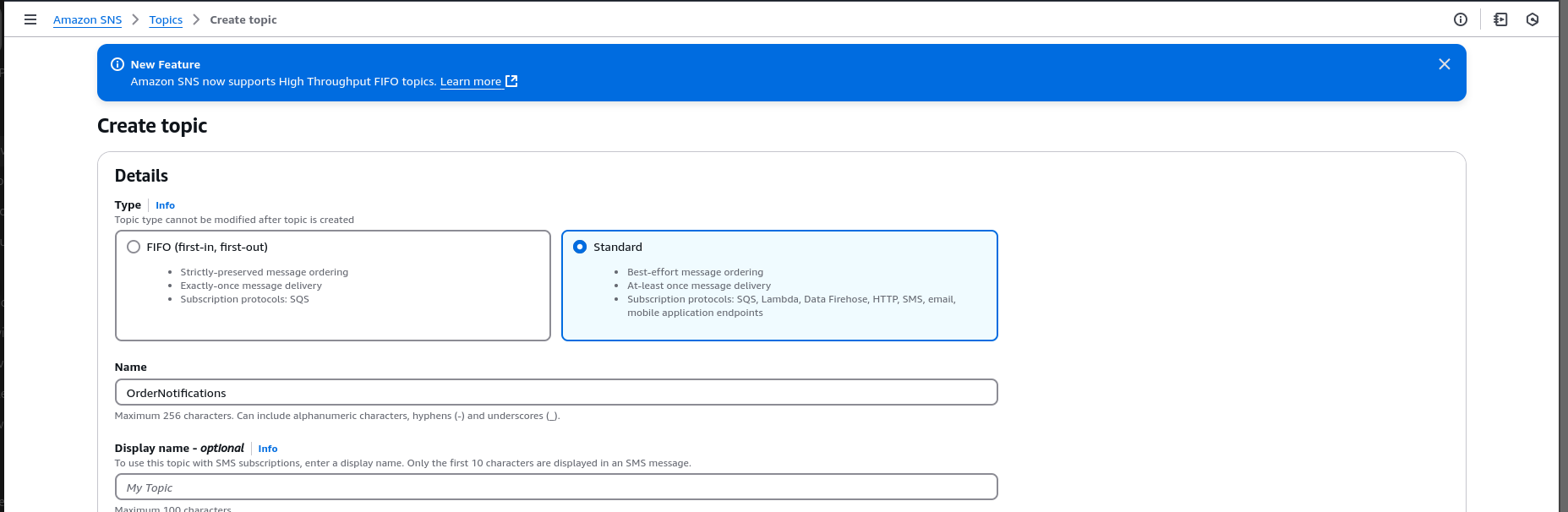
1.Create an SNS Topic
- Navigate to the SNS Console.
- Click Create topic → Choose Standard → Name:
OrderNotifications. - Copy the Topic ARN.
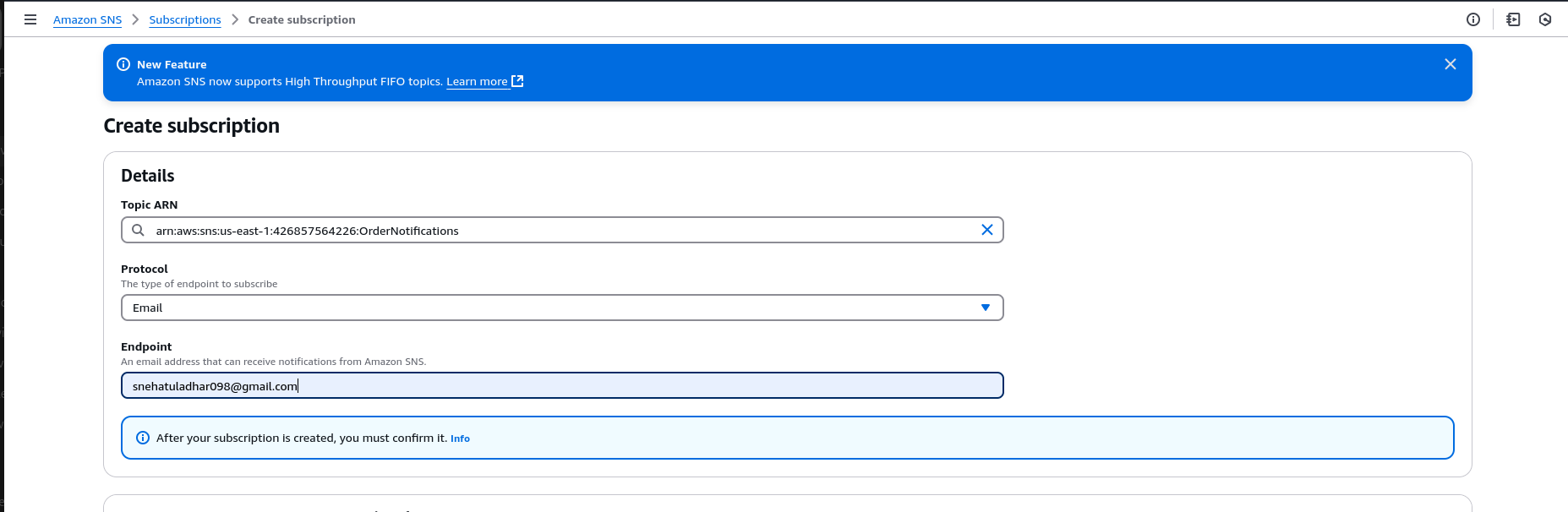
2.Add Subscriptions
Add an email subscription:
- Protocol:
Email - Enter your email address and confirm the subscription from the email.
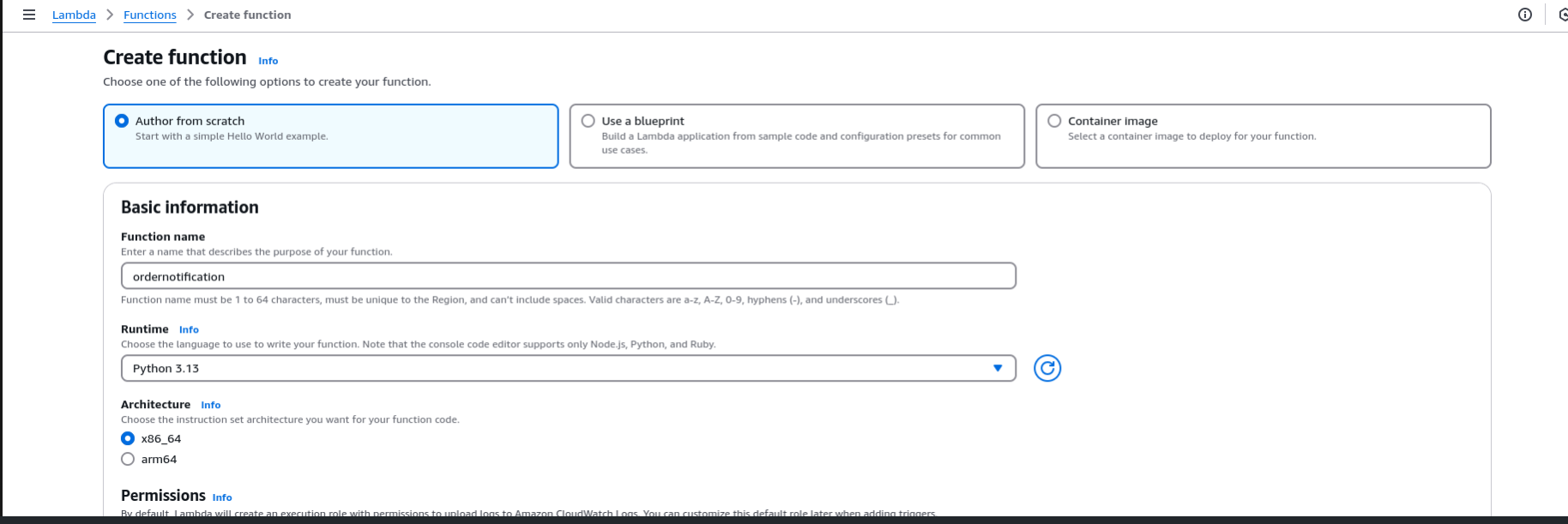
Add a Lambda Subscription
Create a new Lambda function in the AWS Lambda Console:
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Received SNS Event:", json.dumps(event))
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": "Success"}
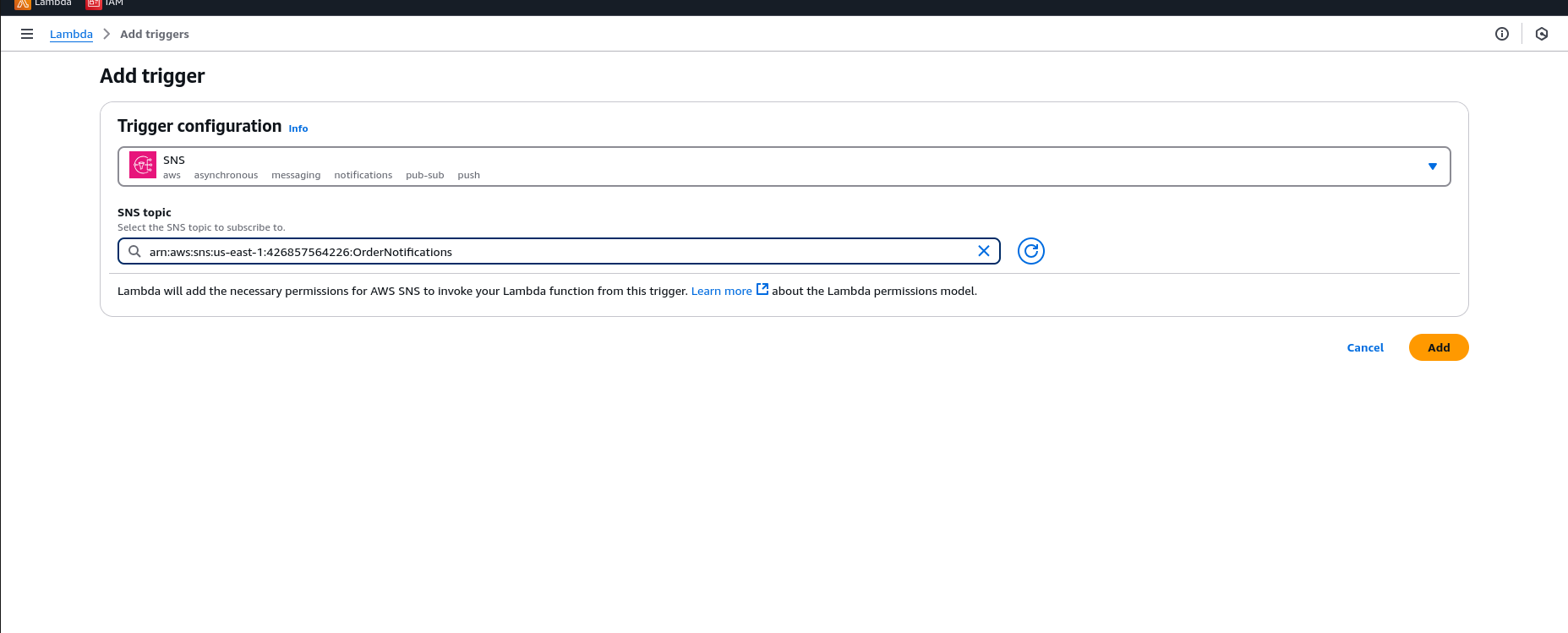
Deploy the function and subscribe it to the OrderNotifications topic. Publish a Message
Go to the SNS Console, select your topic, and publish a test message.
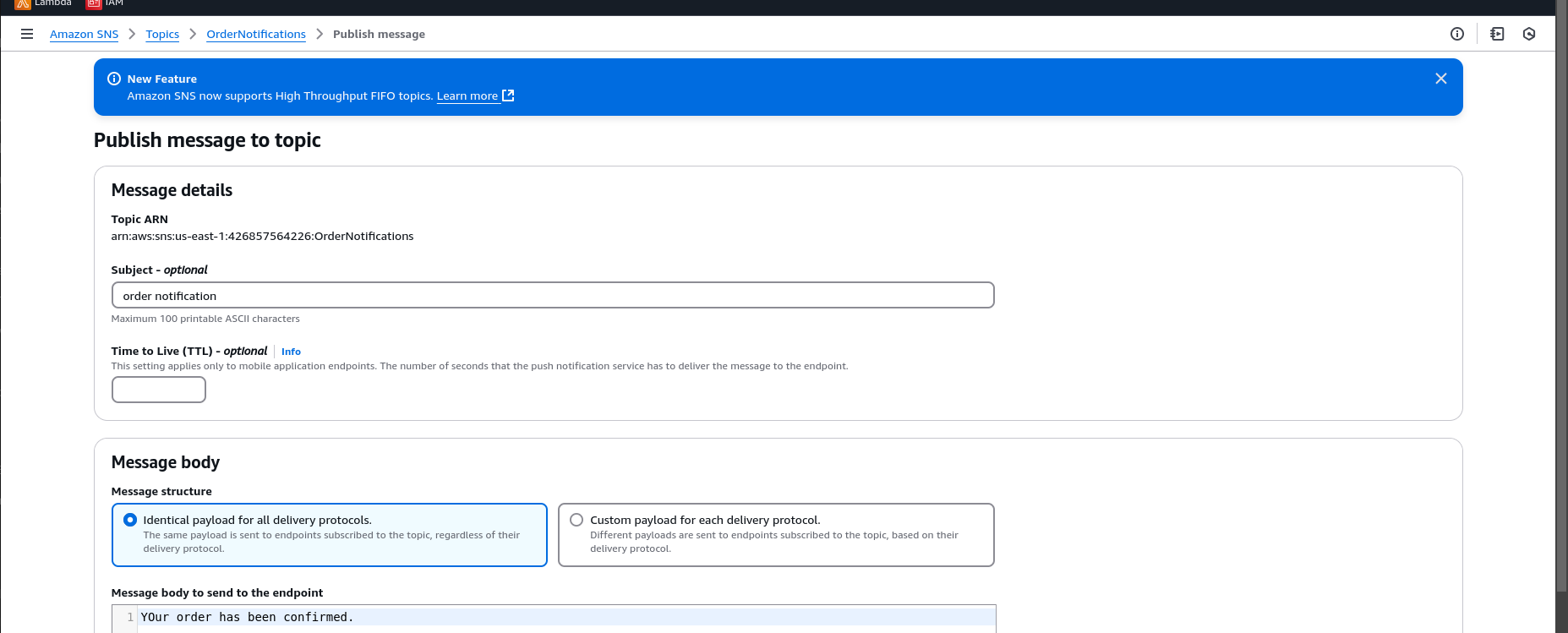
3.Observe the Results
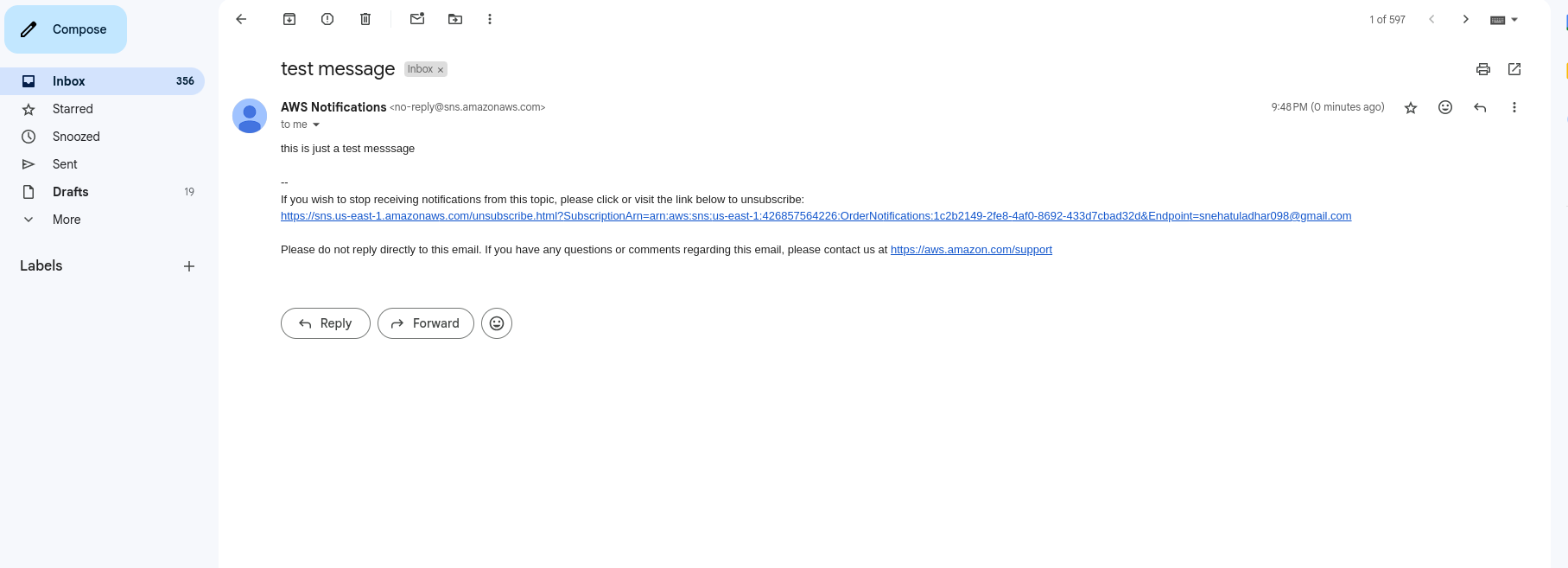
Check your email for the notification.
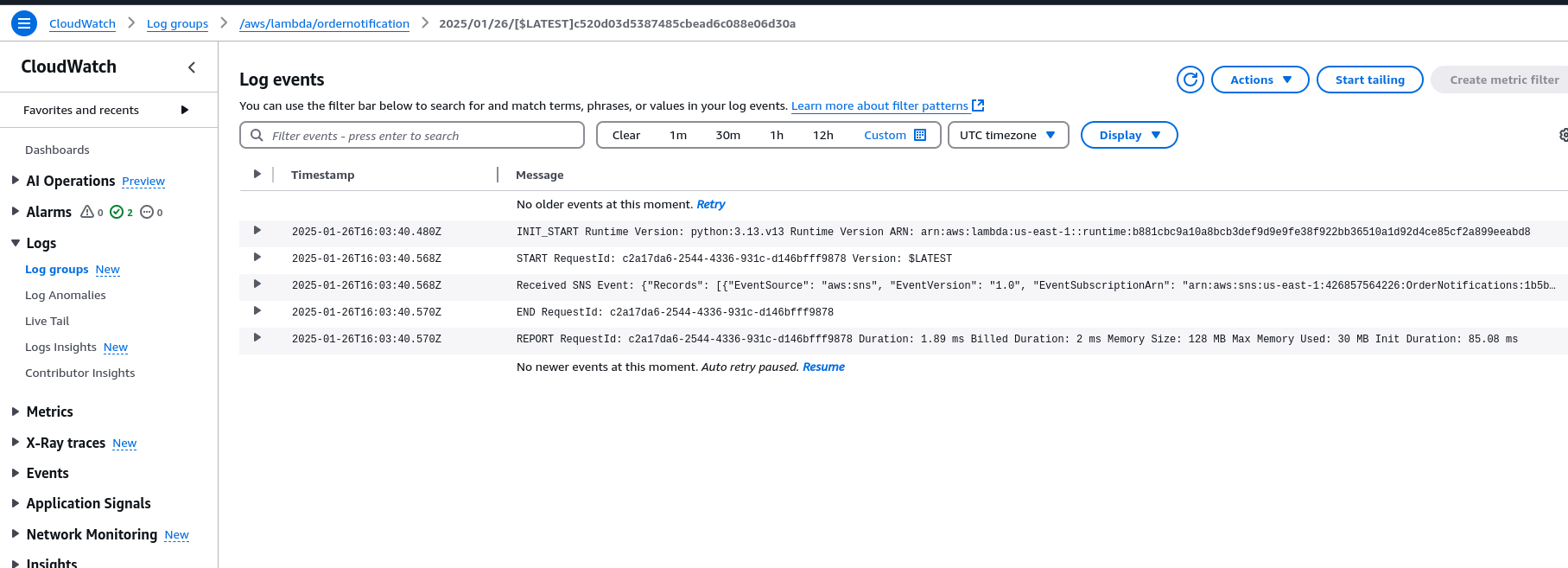
Review the Lambda logs in CloudWatch.
End Result:
- Customer receives an email confirmation.
- Lambda updates inventory or processes the order in real time.
2. Amazon SQS – Queue-Based Messaging
Purpose: Enable decoupling between services through a managed message queue.
Key Features:
- Ensures message durability and at-least-once delivery.
- Enables asynchronous processing at scale.
Example Use Case: Order Fulfillment Pipeline
Process tasks like inventory and payment checks sequentially.
Setup
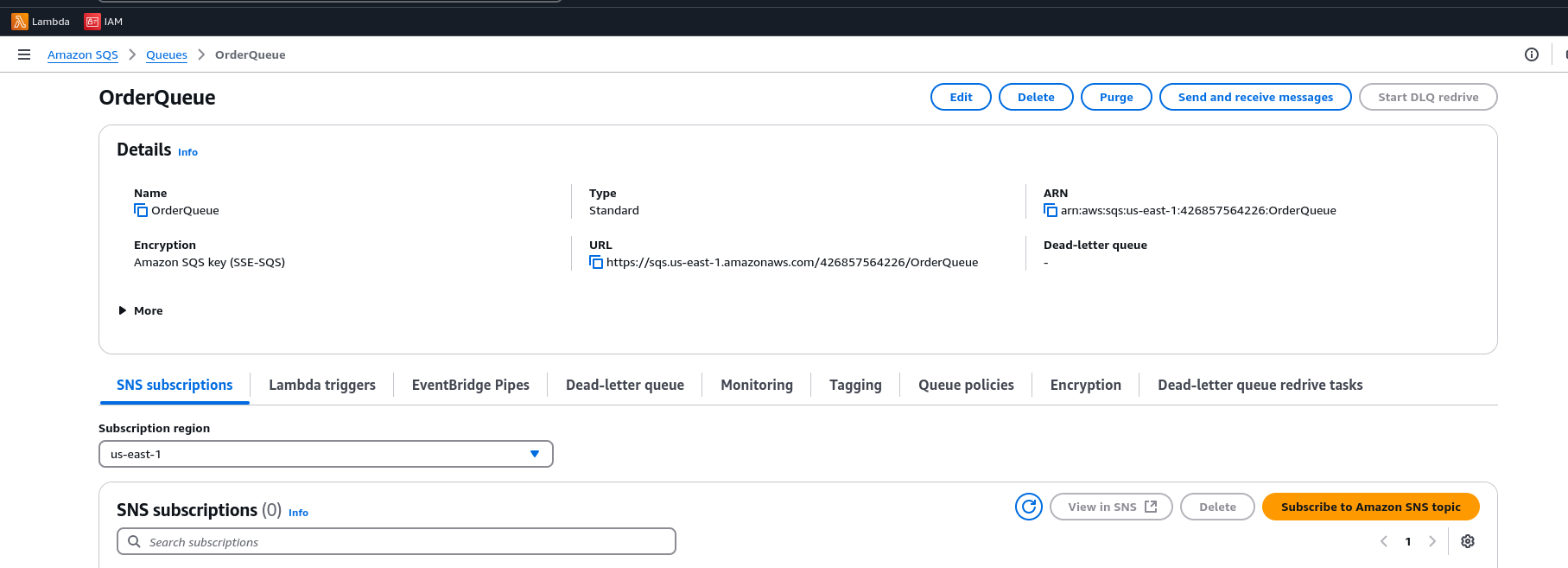
Create an SQS Queue
- Navigate to the SQS Console.
- Click Create Queue → Select Standard Queue → Name it:
OrderQueue.
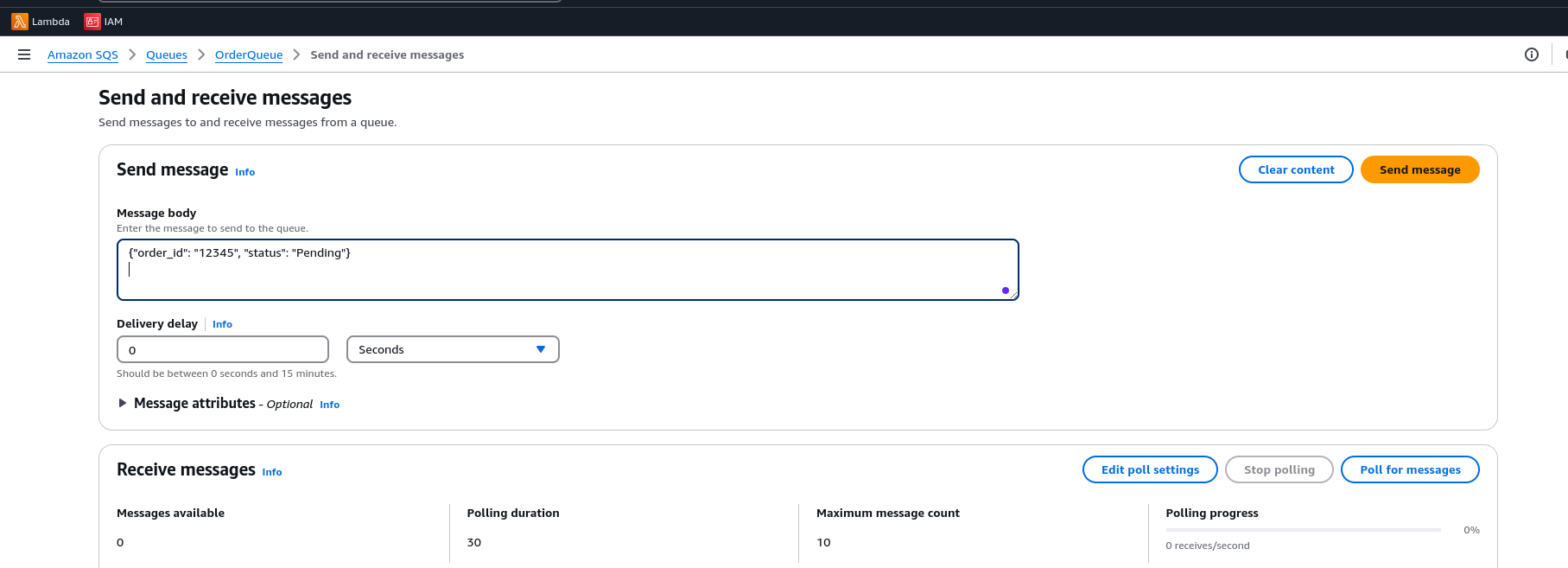
Send a Test Message
Example payload:
{"order_id": "12345", "status": "Pending"}
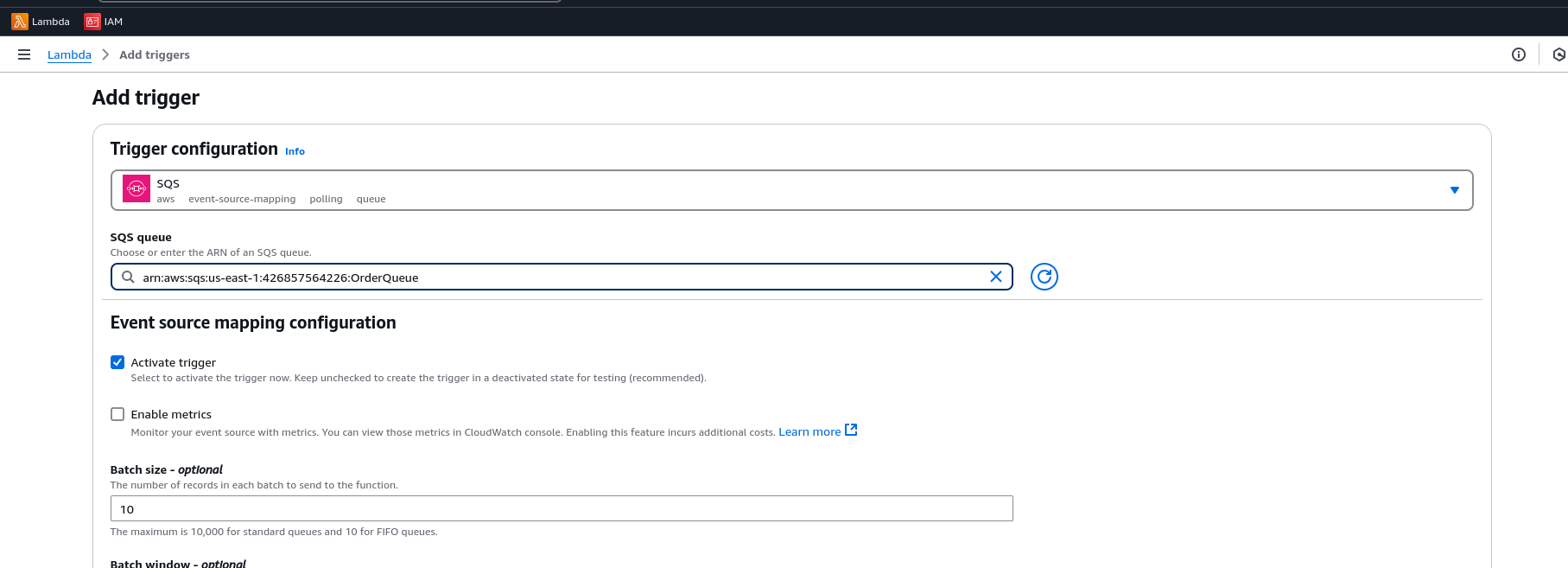
Create a Lambda Function with SQS Trigger
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
for record in event['Records']:
print("Processing message: ", json.dumps(record['body']))
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": "Messages Processed"}
Attach an SQS trigger to the Lambda function by selecting the queue.
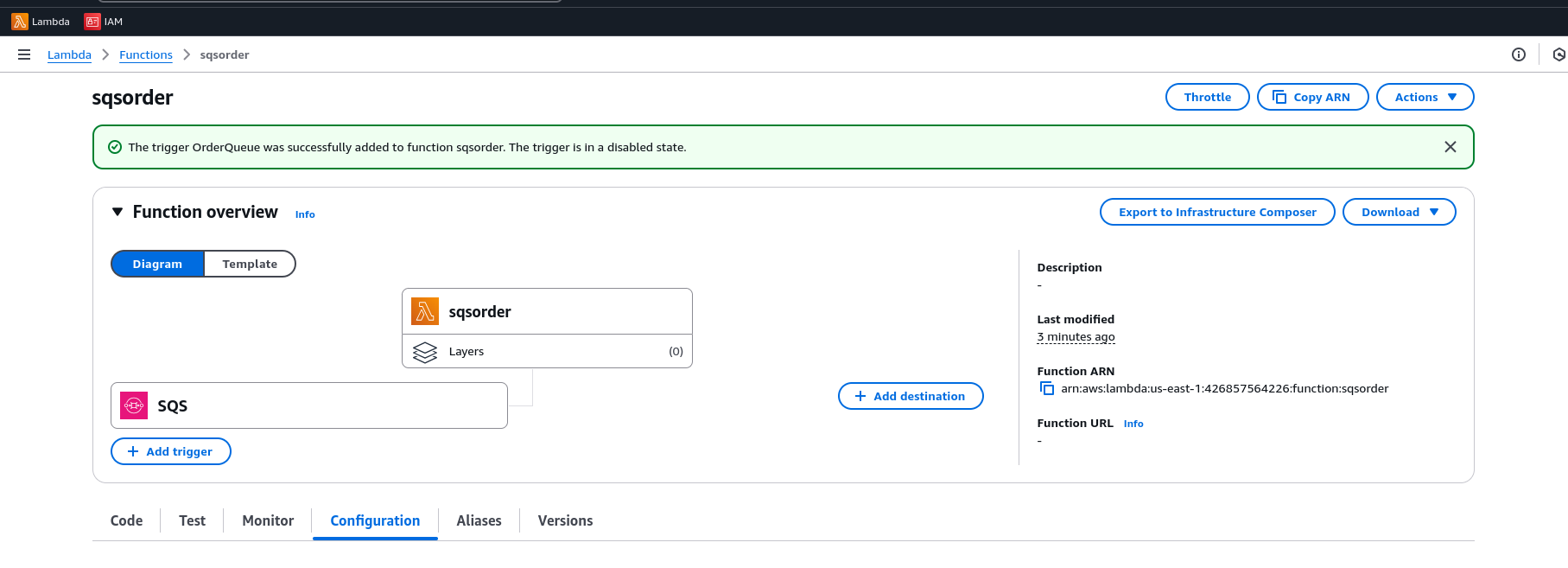
Observe the Results Check logs in CloudWatch for message processing.
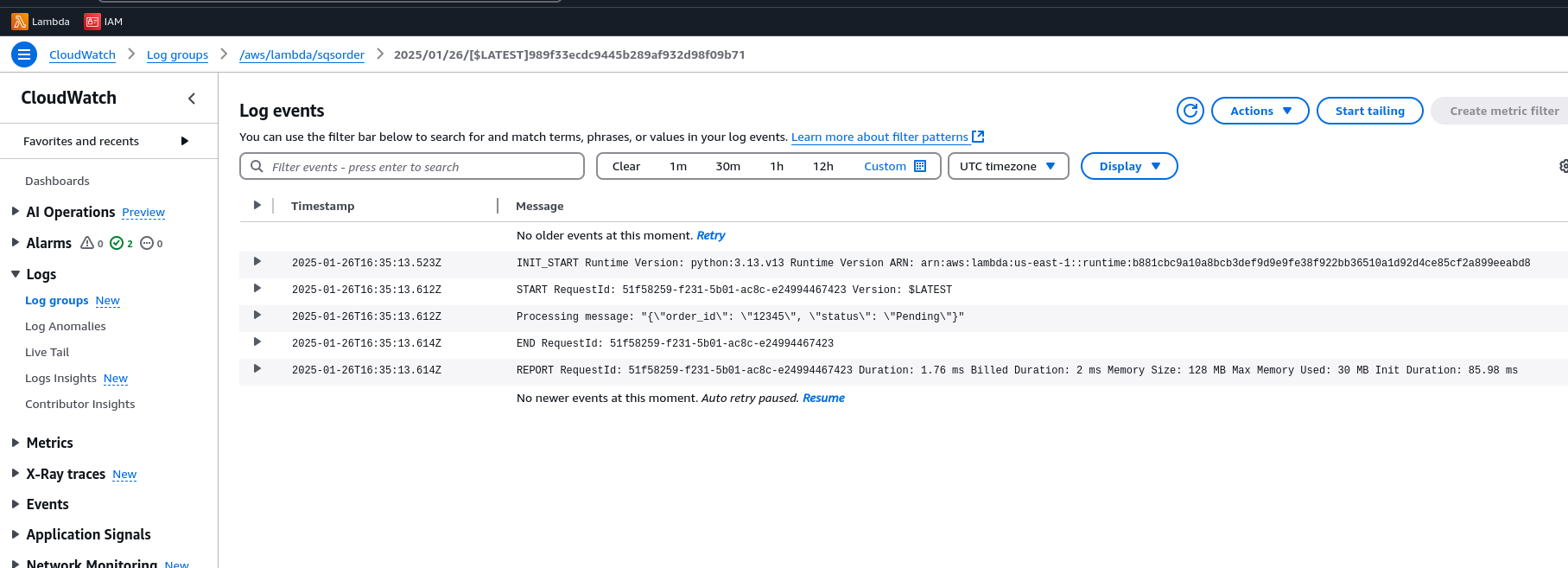
End Result
- Messages are reliably queued and processed
- Lambda scales automatically
- No message loss, and retries are automatic on failure
3. Amazon EventBridge - Event-Driven Architecture
Purpose Route events intelligently between services based on patterns.
Key Features
- Advanced event filtering based on content
- Native integration with 100+ AWS services and third-party SaaS tools
Example Use Case: Real-Time Order Status Updates Trigger a Lambda function when an order's status changes to “shipped” by matching a specific event pattern using EventBridge.
Setup
- Create a Lambda Function
Go to the AWS Lambda Console → Click Create Function
- Name:
OrderShippingHandler - Runtime: Python 3.x
Use the following code:
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Order shipped event:", json.dumps(event))
return {"statusCode": 200, "body": "Order Processed"}
Click Deploy. 2.Create an EventBridge Rule
Go to the EventBridge Console.
Click Create Rule → Name it OrderShippedRule. Description: Trigger shipping when an order status changes to shipped.
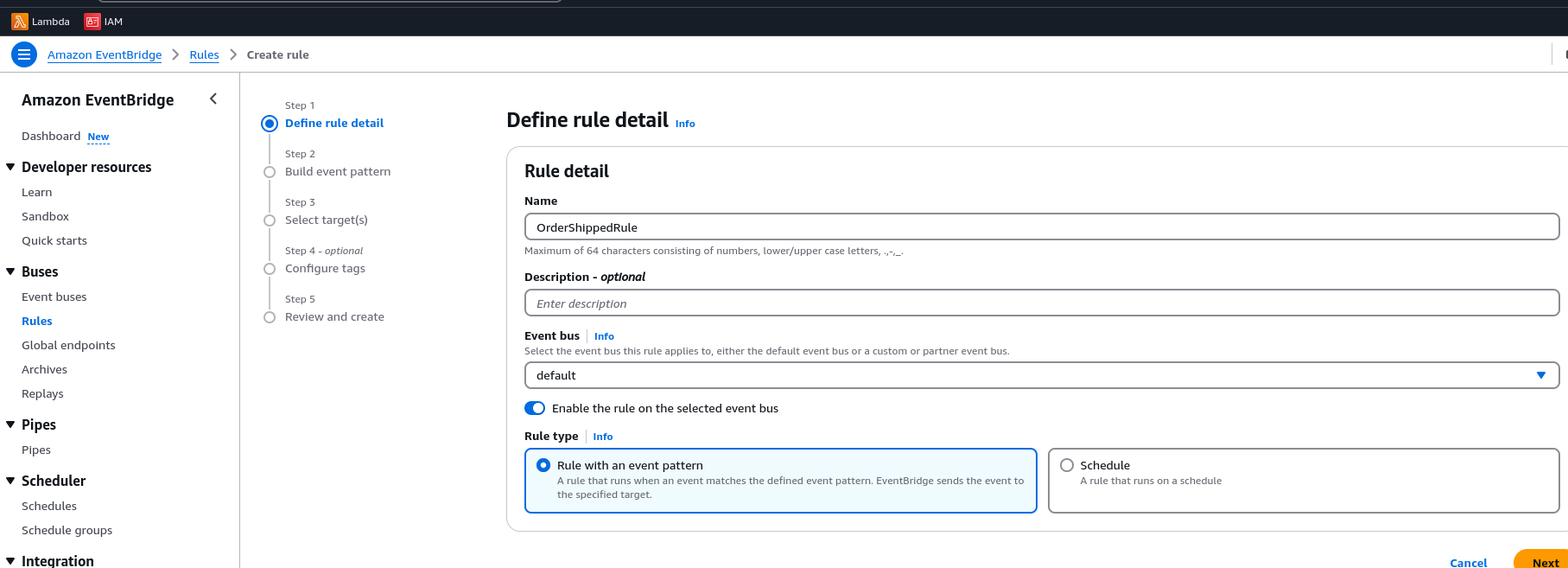
3.Select Event Pattern → Specify the following:
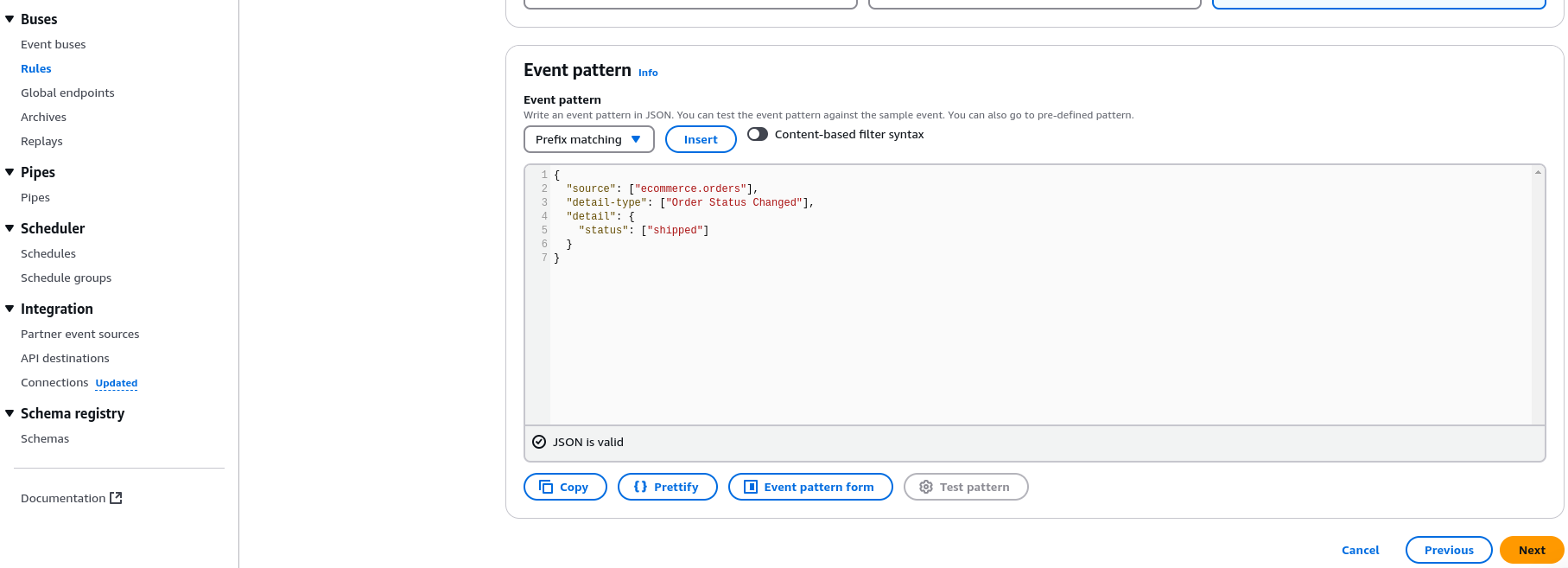
{
"source": ["ecommerce.orders"],
"detail-type": ["Order Status Changed"],
"detail": {
"status": ["shipped"]
}
}
4.Set the Target as the Lambda Function Under Select Targets, choose the following options:
- Target type: AWS service
- Service: Lambda function
- Function:
OrderShippingHandler
5.Send a Test Event Go to the EventBridge Console → Send events.
Enter the following event JSON:
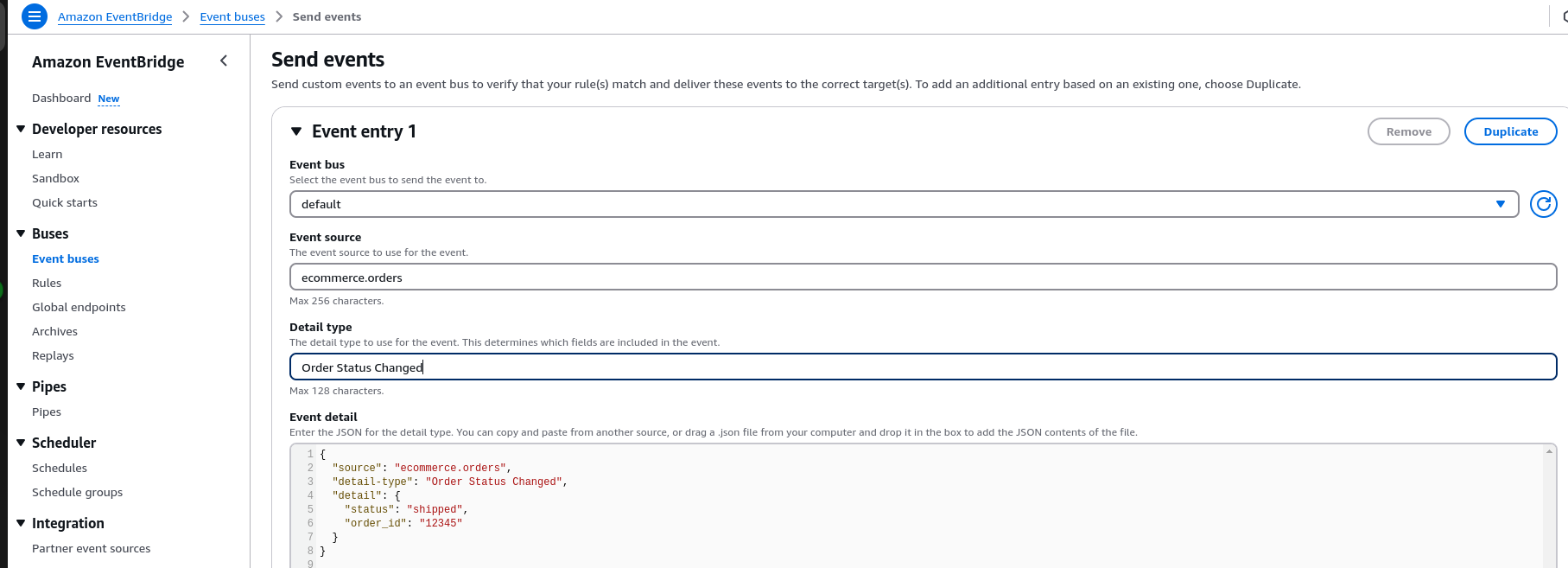
{
"source": "ecommerce.orders",
"detail-type": "Order Status Changed",
"detail": {
"status": "shipped",
"order_id": "12345"
}
}
Verify the Event in CloudWatch
Similarly, check the Lambda logs in CloudWatch for the event details.
- Open the CloudWatch Console.
- Navigate to Logs → Log groups → Lambda → OrderShippingHandler.
- Open the latest log stream.
- Confirm the event was processed and logged correctly.
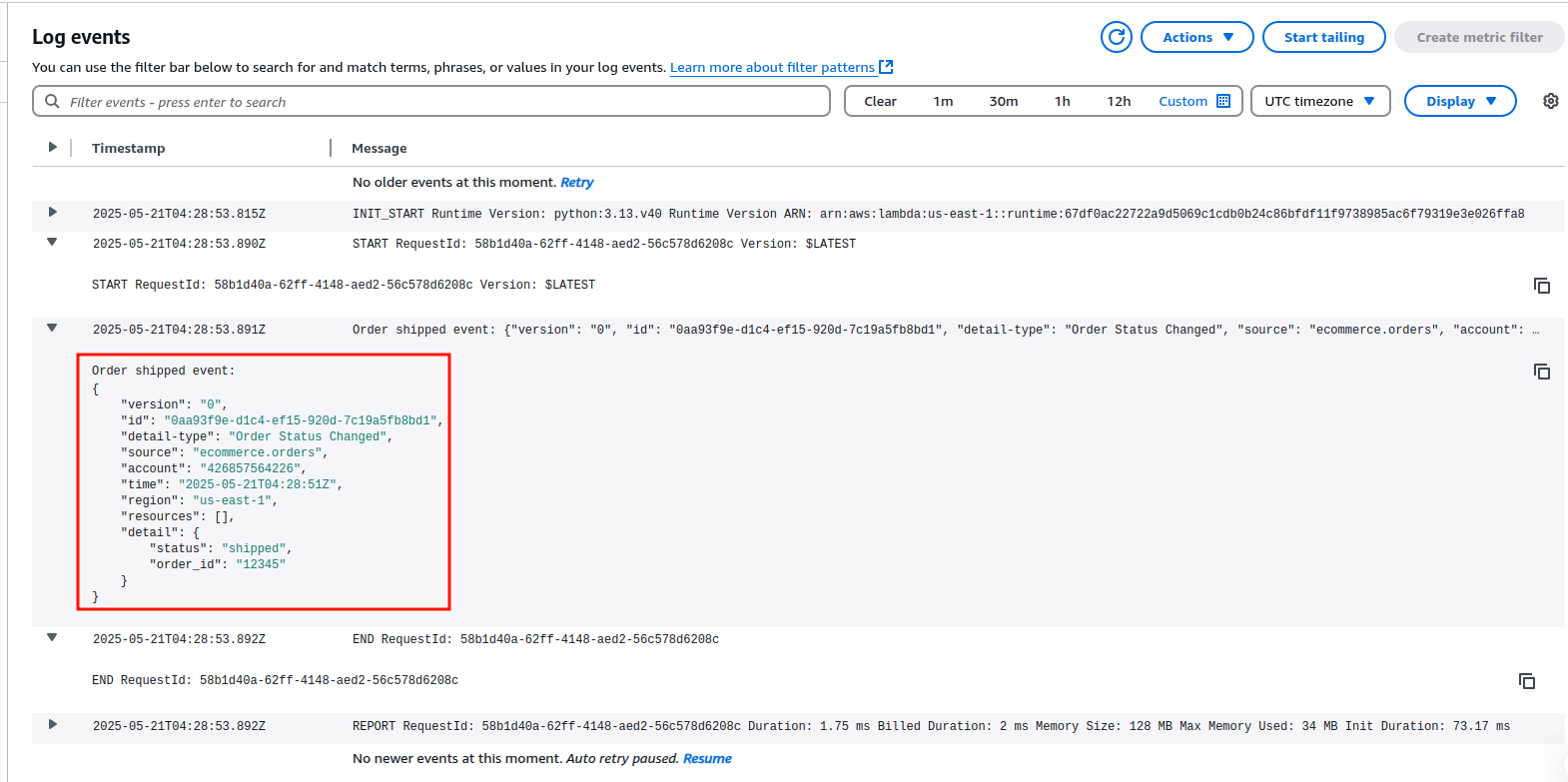
End Result
- When an order is marked as "shipped", EventBridge routes the event.
- Lambda is triggered to initiate shipping workflows automatically.
Service Comparison
| Feature | Amazon SNS | Amazon SQS | Amazon EventBridge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Publish/Subscribe | Point-to-Point (Message Queue) | Event-Driven Routing |
| Fan-out | Yes | No | Yes |
| Event Filtering | No | No | Yes |
| Use Case | Notifications | Task Processing | Complex Workflow Routing |
Integration Strategies with AWS Lambda
- SNS → Lambda: Directly invoke Lambda functions for real-time event processing (e.g., data transformation, analytics).
- SQS → Lambda: Process messages asynchronously with built-in error handling and scaling.
- EventBridge → Lambda: Execute serverless workflows in response to specific events (e.g., security alerts, system state changes).
Best Practices
- Choose SNS for broadcasting events to multiple subscribers.
- Use SQS when you need reliable, ordered, or delayed processing of tasks.
- Leverage EventBridge for routing events across accounts/services or integrating SaaS applications.
- Combine Services: For example, use SNS to fan out events, then SQS to queue tasks for downstream services.
Conclusion
Amazon SNS, SQS, and EventBridge each solve unique challenges in event-driven architectures:
- SNS excels at real-time notifications to distributed systems.
- SQS ensures reliable and scalable task processing.
- EventBridge provides sophisticated event routing for complex workflows.
By strategically combining these services with AWS Lambda, you can build resilient, scalable applications that respond dynamically to changes in your system. Whether you’re coordinating microservices, processing streaming data, or automating workflows, these tools form the backbone of modern cloud-native development.