- Published on
Adding HTTP Security Headers Using Lambda@Edge and Amazon CloudFront
- Authors

- Name
- Sneha Tuladhar
- @
Table of Contents
Introduction
Security headers are HTTP response headers that tell your browser how to handle your site’s content. For example, the X-XSS-Protection header helps prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks by blocking pages if suspicious scripts are detected. It works in browsers like Internet Explorer and Chrome.
Protection against cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, and data injection attacks is made easy with HTTP security headers. Security headers have been attached to the CloudFront distribution through Lambda@Edge to enhance protection.
CloudFront either caches content from the server or pulls it from S3 if not cached. Lambda@Edge allows modifications to headers before data is sent to users, improving security and reducing latency.
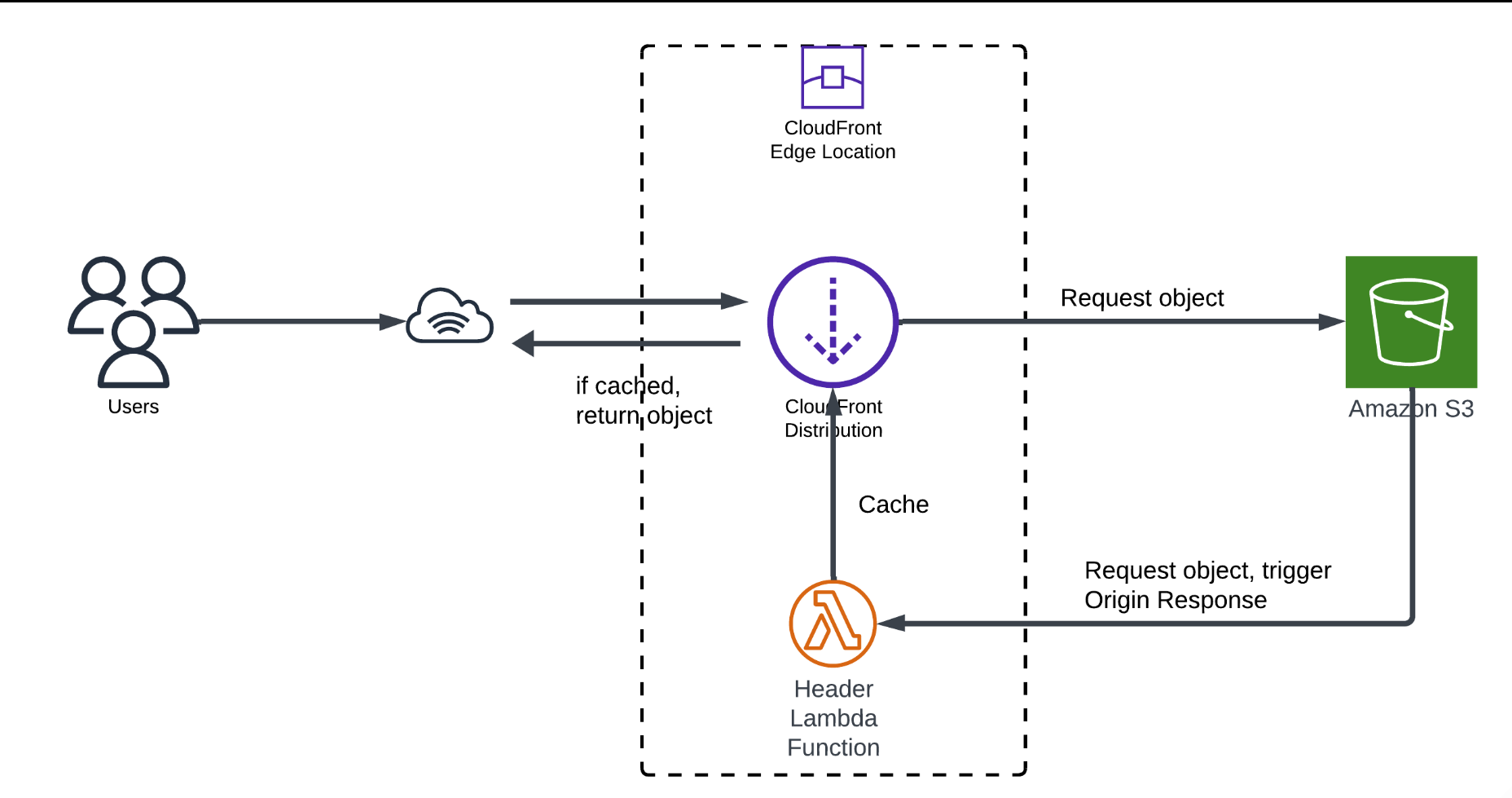
Prerequisites
- An Amazon S3 bucket hosting your website.
- A CloudFront distribution configured to serve content from the S3 bucket.
- AWS Lambda access with permissions to create functions.
Steps to Add Security Headers
1. Create a Lambda Function
- Open the AWS Lambda Console in US East (N. Virginia) - us-east-1.
- Click Create function.
- Select Use a blueprint.
- Enter a function name and select Node.js 16.x as the runtime.
- Under Permissions, choose Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions.
- Click Create function.

2. Add Security Headers Code
Scroll to the Code Source section and replace index.js with:
'use strict';
export const handler = async (event) => {
// Get contents of response
const response = event.Records[0].cf.response;
const headers = response.headers;
// Set new headers
headers['strict-transport-security'] = [{
key: 'Strict-Transport-Security',
value: 'max-age=63072000; includeSubdomains; preload'
}];
headers['content-security-policy'] = [{
key: 'Content-Security-Policy',
value: "default-src 'none'; img-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; object-src 'none'"
}];
headers['x-content-type-options'] = [{ key: 'X-Content-Type-Options', value: 'nosniff' }];
headers['x-frame-options'] = [{ key: 'X-Frame-Options', value: 'DENY' }];
headers['x-xss-protection'] = [{ key: 'X-XSS-Protection', value: '1; mode=block' }];
headers['referrer-policy'] = [{ key: 'Referrer-Policy', value: 'same-origin' }];
// Return modified response
return response;
};
3. Deploy and Test
-1.Click the Test tab. -2.Click Create new test event. -3.Enter an Event Name and modify it. Here’s a sample test event you can use in the AWS Lambda console: Terraform snippet:
{
"Records": [
{
"cf": {
"config": {
"distributionId": "EXAMPLE123"
},
"request": {
"uri": "/index.html",
"method": "GET",
"headers": {
"host": [
{
"key": "Host",
"value": "example.cloudfront.net"
}
]
}
},
"response": {
"status": "200",
"statusDescription": "OK",
"headers": {
"cache-control": [
{
"key": "Cache-Control",
"value": "max-age=100"
}
],
"content-type": [
{
"key": "Content-Type",
"value": "text/html"
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
- Click Create and then Test to execute the function.
- Check the Execution result section to see the output and logs.
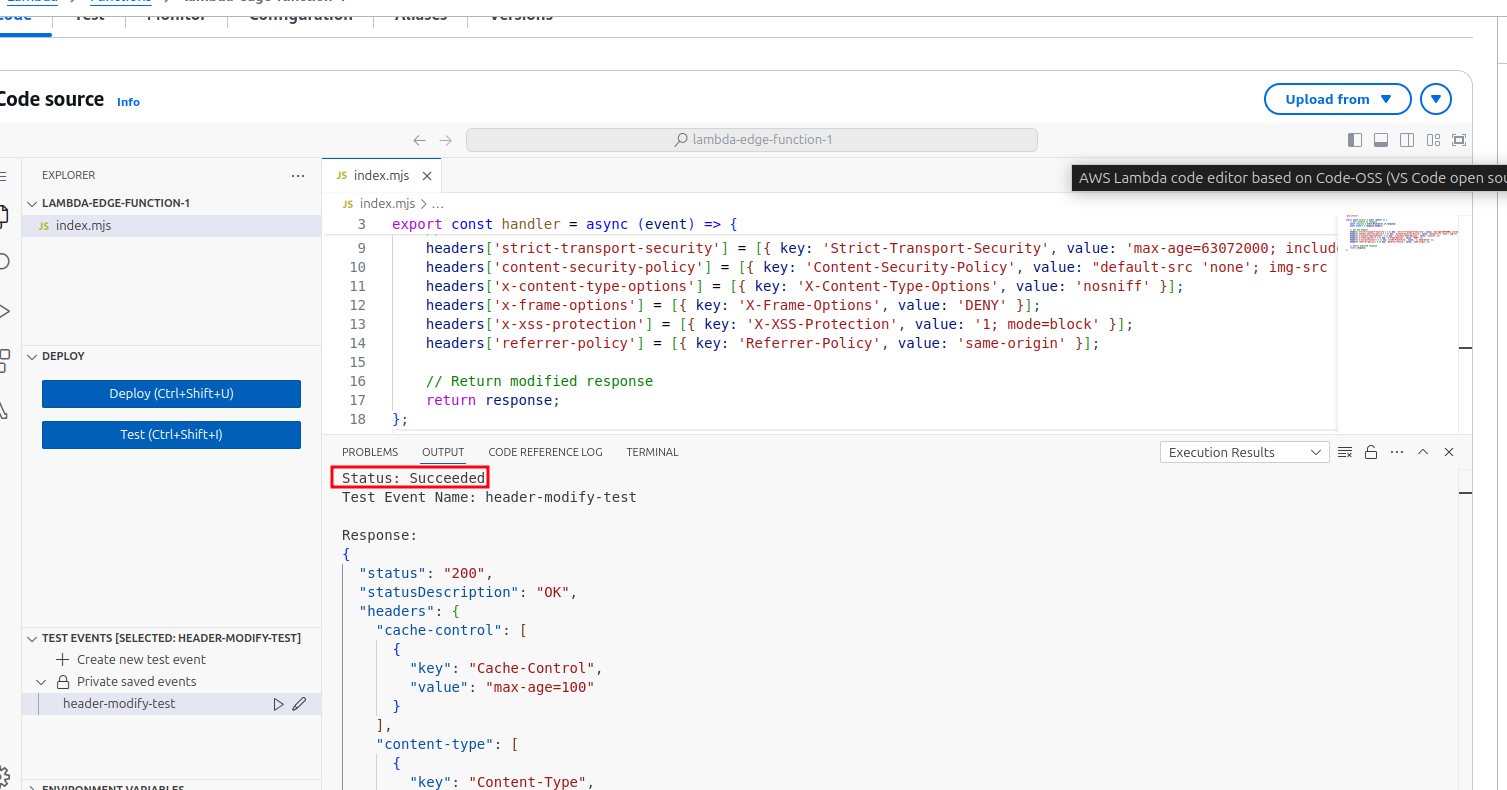
4. Configure CloudFront Trigger
- Navigate to the Lambda function you created.
- Click Add trigger → Choose CloudFront.
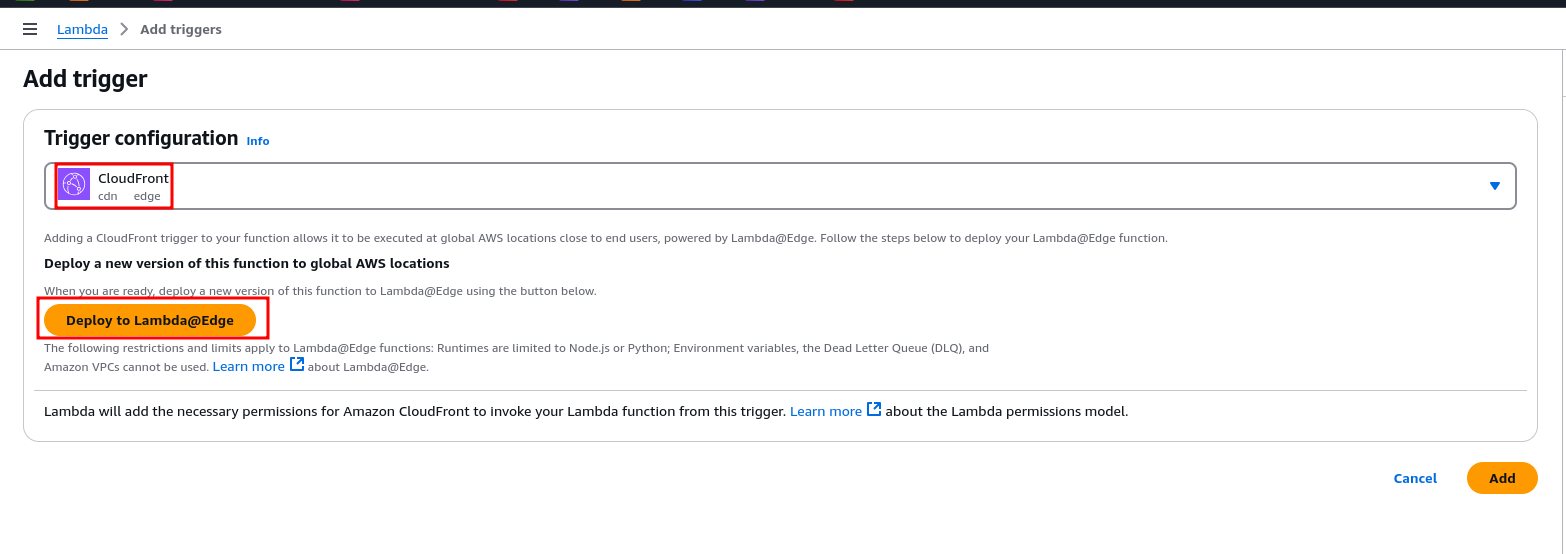
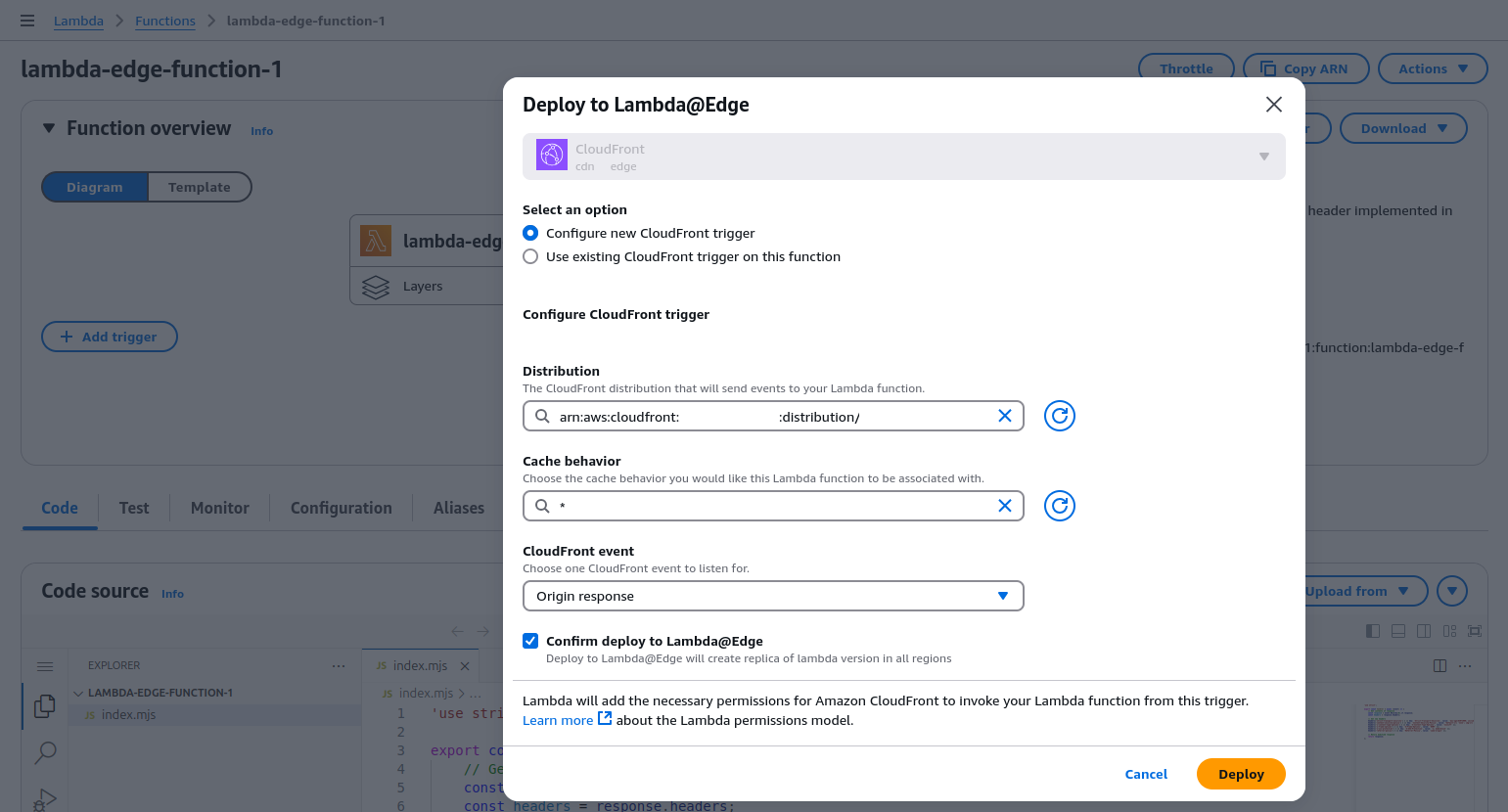
- Select the CloudFront distribution serving your website.
- Set Cache Behavior to
*. - Choose Origin Response as the event.
- Enable Replicate across regions.
- Click Add.
5. Deploy and Verify
- Wait for CloudFront to deploy the updated configuration (~2–7 minutes).
- Open your website in a browser.
- Open Developer Tools → Network Tab.
- Reload the page and inspect the response headers.
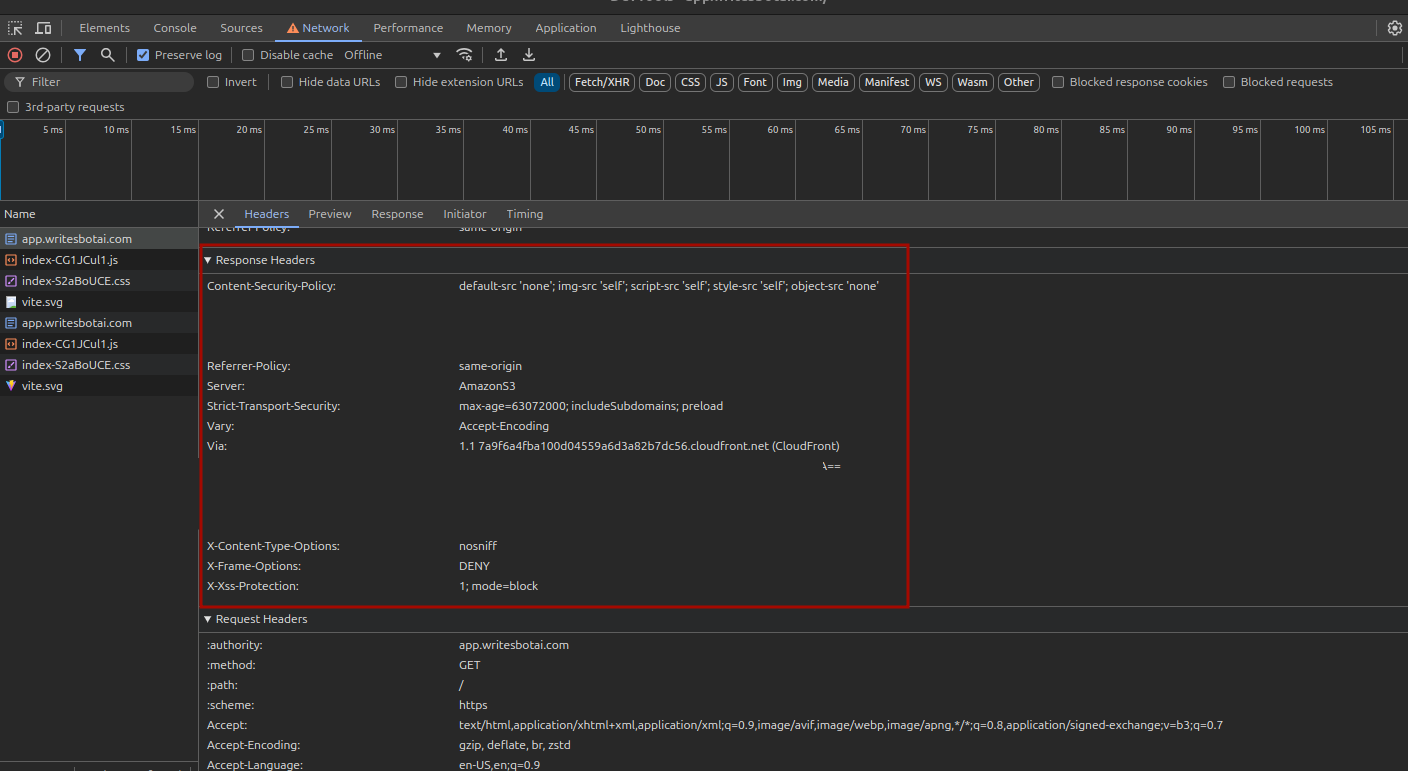
6. Test Security Headers
- Visit Mozilla Observatory HTTP Header Security Test.
- Enter your website URL and run a scan.
- Check the security rating.
Monitoring and Debugging
- Check Amazon CloudWatch Logs for Lambda function execution details.
- Verify CloudFront distribution status (should be Deployed).
- Ensure Lambda executes on Origin Response events.
- Debug Content Security Policy (CSP) issues by inspecting blocked requests in browser Developer Tools.
- Modify the
Content-Security-Policyheader as needed to allow necessary resources while maintaining security. - Clear CloudFront Cache (Invalidate) when required.
💡 Note: Invalidating everything (/*) can be expensive if done frequently. Target only specific changed files when possible.
Conclusion
By configuring AWS Lambda@Edge to inject HTTP security headers:
- You have strengthened your website’s defenses against various online threats.
- Security headers protect user data and maintain a secure browsing environment.
- Regularly monitor CloudWatch logs and review security header performance using tools like Mozilla Observatory.
- Manage your CloudFront cache efficiently to ensure updates take effect.
With these security measures in place, your website is more secure and reliable for users.