- Published on
Enforcing AWS Compliance with AWS Config and Terraform
- Authors

- Name
- Sneha Tuladhar
- @
Table of Contents
- The solution to the problem by AWS.
- Key Capabilities
- Core Workflow
- Enabling AWS Config
- AWS Config Terraform Implementation
- The Usage of AWS Config Components.
- Scaling using Conformance Packs
- Outcomes and Benefits
- Conclusion
The need to maintain the configurations, apply the tagging policies, and demonstrate the compliance at the auditing stage may become overwhelming in dynamic and expanding cloud environments. The most frequent questions are raised, including:
- What resources are missing the tags required such as Environment or Owner?
- The question of knowing what a resource appeared like last week?
- Where can we manage to monitor the changes and implement policies automatically in all the accounts?
It is inaccurate and time-consuming to handle compliance and configurations manually in a number of accounts in AWS. In order to overcome these issues, the team introduced the use of AWS Config, which is a powerful service which monitors, audits, and evaluates the configurations of the AWS resources on a continuous basis. It can be used together with Terraform in order to automate infrastructure-as-code and ensure compatibility at the beginning
The solution to the problem by AWS.
AWS Config is used to monitor, audit, and evaluate continuing resources of AWS. Terraform ensures compliance since the functionality establishes integrity and compliance at scale.
The AWS AWS Config and CloudTrail may resemble each other but they are contrasting:
- AWS Config → Tracks records configuration at some time..
- CloudTrail → Records API calls and actions (who, what, when).
The combination renders them a whole picture on compliance and auditing.
Key Capabilities
- Resource Timeline: Timeline of configuration changes.
- Compliance Rules: 200+ AWS-managed rules (e.g.,
ec2-instance-no-public-ip) - Conformance Packs: Ready to use compliance frameworks (HIPAA, NIST 800-53)
- Advanced Queries: e.g.,
"Show unencrypted S3 buckets" - Multi-Account Aggregation: Data collection of compliance is centralized.
Core Workflow

- Configuration Recorder → Records changes in resources.
- Delivery Channel → Delivers snapshots to S3/SNS.
- Config Rules → - Checks the correspondence, of resources to requirements.
Enabling AWS Config
Three approaches exist:
- AWS Control Tower – Auto-enabled in landing zones
- Manual Implementation – One-click wizard in AWS Console
- Infrastructure-as-Code (Terraform) – Best approach to scalability.
AWS Config Terraform Implementation
AWS Config was used to impose necessary tagging in every environment, which was implemented through Terraform.
⚠️ Critical Notes
- Region-specific → should be activated regionally.
- No retroactive tracking → just monitors upon enablement.
- Cost model → charged per billed active rule x resource assessments.
Step 1: S3 Bucket for Config Logs
Create a S3 bucket using a reusable Terraform module to store all AWS Config snapshots and compliance logs.
module "config_logs_s3" {
source = "./modules/terraform-aws-s3-module"
bucket = "${module.naming.resources.s3.name}-config-logs-bucket"
force_destroy = false
versioning = {
enabled = true
}
attach_policy = true
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.aws_config_s3_policy.json
tags = module.naming.default_tags
}
Step 2: AWS Config IAM Policy of S3 bucket.
This policy provides AWS Config with access to:
1.Review bucket permissions 2.Verify bucket existence 3.Deliver configuration snapshots and logs
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "aws_config_s3_policy" {
statement {
sid = "AWSConfigBucketPermissionsCheck"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["config.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = [
"s3:GetBucketAcl",
"s3:GetBucketLocation"
]
resources = [
aws_s3_bucket.config_bucket.arn
]
}
statement {
sid = "AWSConfigBucketDelivery"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["config.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = [
"s3:PutObject"
]
resources = [
"${aws_s3_bucket.config_bucket.arn}/*"
]
}
}
Step 3:Setting up of AWS Config Core Components.
- Configuration Recorder Recorder Logs notifications of modifications to supported types of resources in each region.
resource "aws_config_configuration_recorder" "main" {
name = "default"
role_arn = aws_iam_role.aws_config.arn
recording_group {
all_supported = true
include_global_resource_types = true
}
}
- Delivery Channel Transfers configuration snapshots and compliance information to the configured S3 bucket.
resource "aws_config_delivery_channel" "main" {
name = "default"
s3_bucket_name = module.config_logs_s3.s3_bucket_id
depends_on = [aws_config_configuration_recorder.main]
}
- Recorder Activation Triggers configuration recorder.
resource "aws_config_configuration_recorder_status" "main" {
name = aws_config_configuration_recorder.main.name
is_enabled = true
depends_on = [aws_config_delivery_channel.main]
}
Step 4:AWS Config Rule: Enforce Required Tags
Having AWS Config turned on and tags being recorded, now a Config Rule is set, which verifies that certain types of resources possess the necessary tags.
resource "aws_config_config_rule" "required_tags" {
name = "${module.naming.resources.prefix.name}-required-tags-compliance"
description = "Ensure AWS resources are tagged according to compliance requirements"
source {
owner = "AWS"
source_identifier = "REQUIRED_TAGS"
}
input_parameters = jsonencode({
tag1Key = "Environment",
tag2Key = "Project",
tag3Key = "CreatedBy",
tag4Key = "Application",
tag5Key = "Compliance",
tag6Key = "Terraform"
})
scope {
compliance_resource_types = [
"AWS::S3::Bucket",
"AWS::RDS::DBInstance",
"AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup",
"AWS::EC2::VPC"
]
}
depends_on = [aws_config_configuration_recorder_status.main]
}
What This Rule Verifies
This AWS-managed rule (REQUIREDTAGS) verifies the presence of the required tags of the specified resource types (the Environment and Owner and others that are defined).
In case one of the specified tags is missing in a resource, AWS Config will treat it as NONCOMPLIANT.
This assists in establishment of governance, allocation of costs, security audit and other organizational policies based on resource tagging.
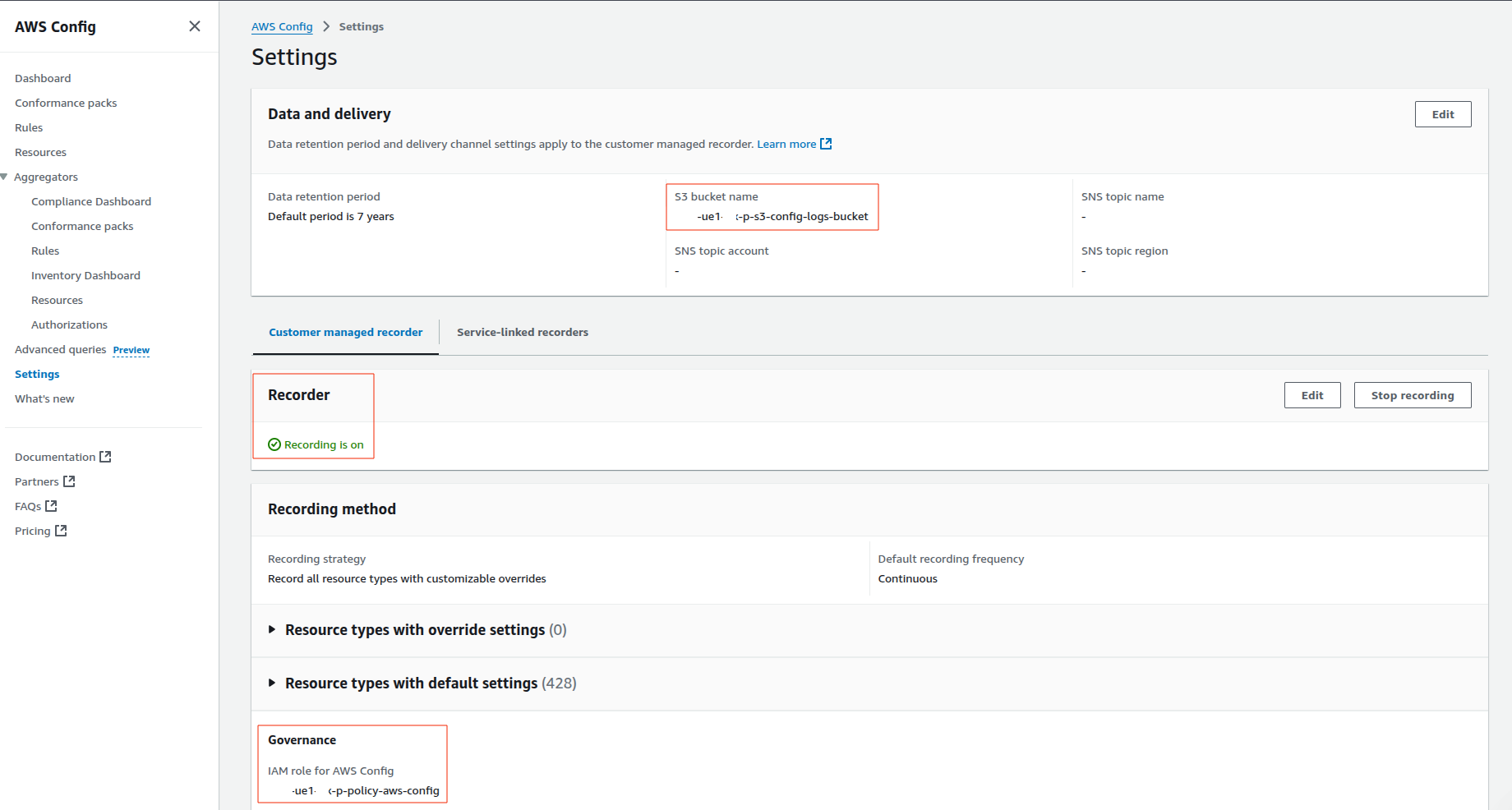
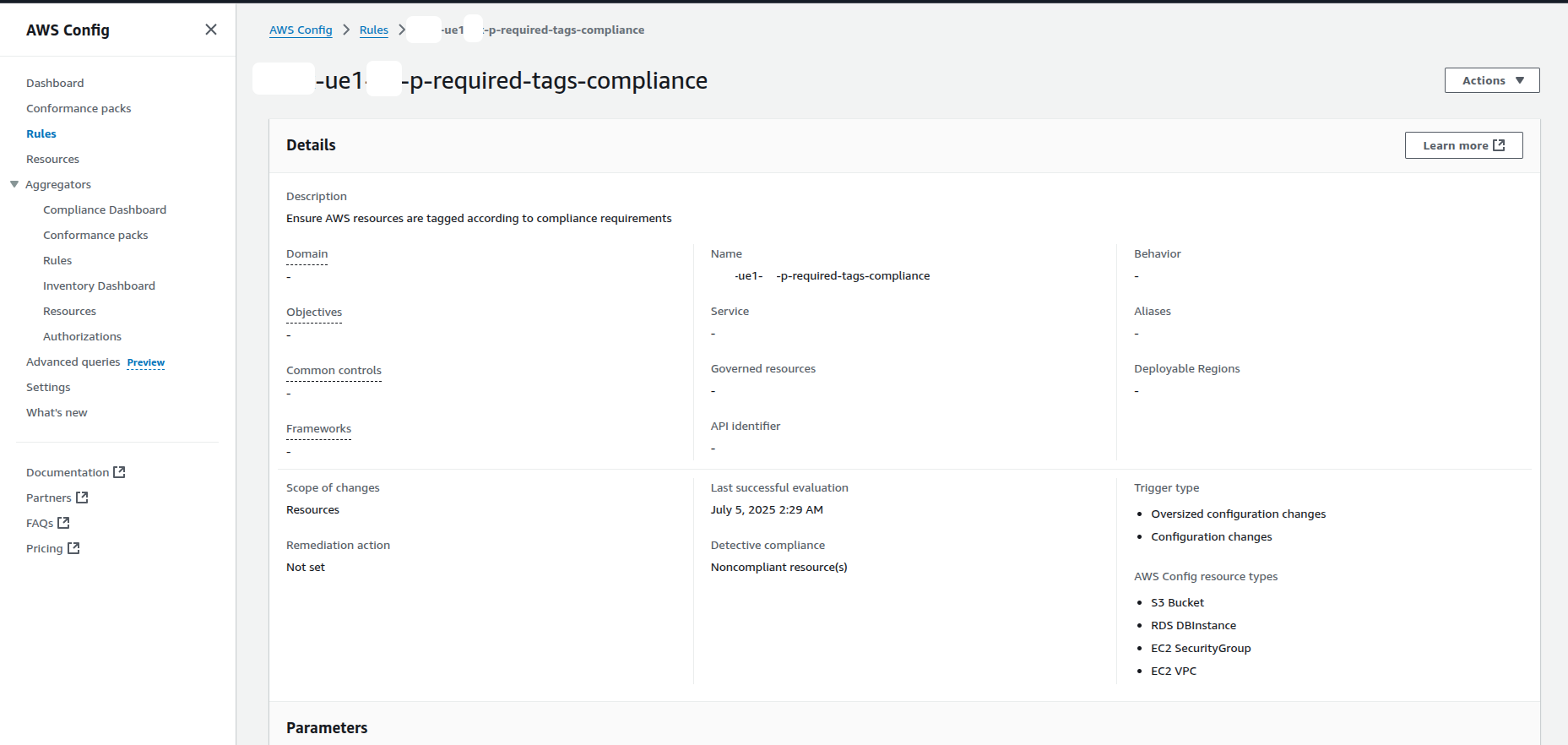
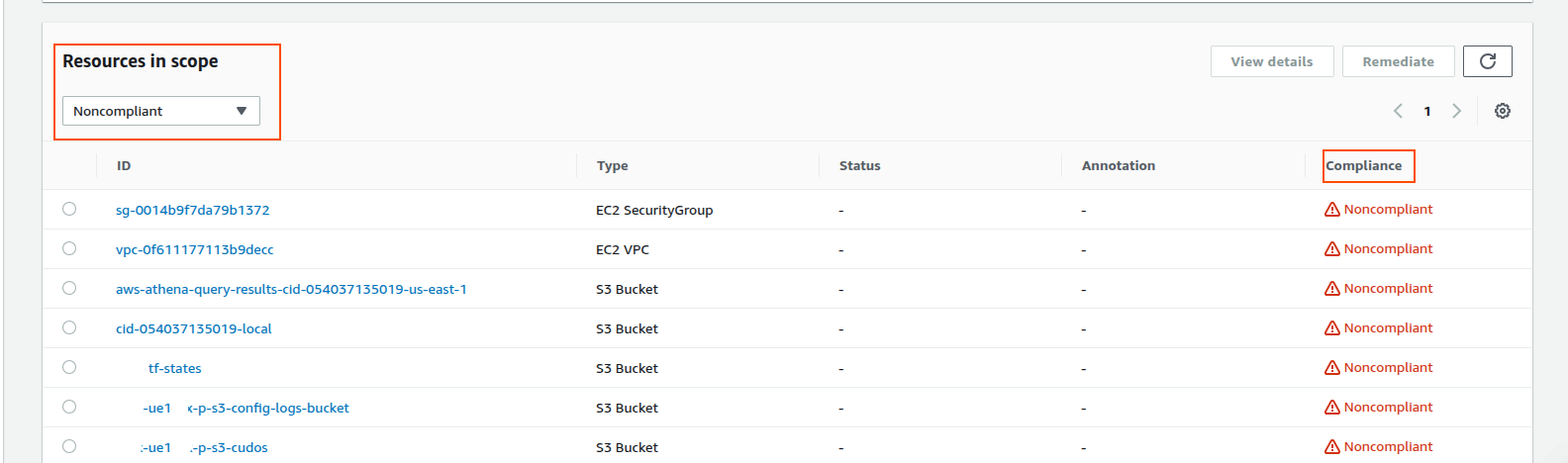
The Usage of AWS Config Components.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Configuration Recorder | Logs the change in resource configuration. |
| Delivery Channel | Transfers content to S3 and SNS. |
| Config Rule | Checks necessary tags. |
| S3 Bucket | Holds logs and snapshots. |
| IAM Role/Policy | Such permissions provide AWS Config authorization to write and provide configuration information. |
Scaling using Conformance Packs
In case the organization has wider requirements in regard to compliance in several accounts or standards (e.g., CIS, HIPAA, NIST 800-53), Conformance Packs offer scalable frameworks.
A Conformance Pack refers to a YAML-Store of several Config Rules and optional remedial actions. Although not essential in the above simple tagging case, they are the best when it comes to realization of complete compliance structure in an enterprise setting.
Outcomes and Benefits
Having AWS Config and Terraform, the following was achieved in the organization:
- Automated observance of non-compliant resources
- Dynamic resource configuration observation.
- Monitoring enforcement in environments.
- Protective delivery and storage of audit reports.
- A basis to scale compliance to Conformance Packs.
Conclusion
AWS Config facilitates compliance as a continuous process which is automated unlike the previous manual process which was done periodically. To have this visibility with regard to governance, AWS Config offers consistency and ensures that all resources share similar tags, which are helpful in organizational policies and cost allocation. AWS Config helps achieve operational excellence by offering the teams with the option to re-create historical status of their resources and conduct adequate root cause analysis.Also, it is more secure as it has the ability of recognizing publicly available buckets accentuated by Amazon S3 or un-encrypted volumes. Besides, it simplifies cost optimization since it detects and removes any untagged or improperly configured resources. With AWS config enabled, your cloud is automatically safe and compliant.